Beyond Dawlish
SAP BASIS Upgrades And Migrations: A Step-by-Step Guide
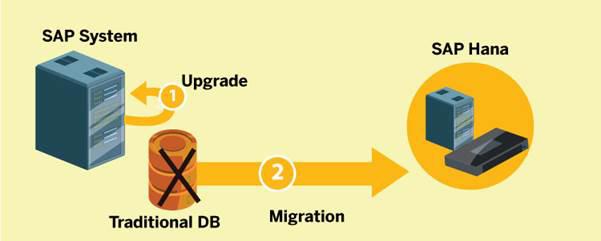
Upgrading and migrating SAP BASIS is a critical task for ensuring system efficiency, security, and compliance. Whether upgrading within the same environment or migrating to a new infrastructure, following a structured approach is essential. Enrolling in an SAP BASIS Course provides hands-on expertise in system administration, installation, upgrades, and migrations, equipping professionals with the necessary skills to handle complex SAP environments effectively.
SAP BASIS Upgrade vs. Migration: Differences
|
Factor |
Upgrade |
Migration |
|
Definition |
Moving to a newer SAP version |
Moving SAP system to a new platform |
|
Scope |
Software enhancements, patches |
Infrastructure change, OS/DB migration |
|
Downtime |
Minimal if planned properly |
Can be significant depending on data volume |
|
Risk Level |
Moderate |
High due to data transformation |
|
Performance |
Improved due to feature enhancements |
Depends on target system efficiency |
An SAP BASIS Course equips professionals with the skills to execute upgrades and migrations with minimal risk, ensuring system stability and enhanced performance.
Step-by-Step Process for SAP BASIS Upgrade

Assessment & Planning
Analyze current SAP system version.
Check SAP support and compatibility for upgrades.
Create a backup strategy.
Sandbox Upgrade
Perform a test upgrade on a sandbox system.
Identify potential issues before production deployment.
Technical Upgrade Execution
Implement patches, kernel updates, and database upgrades.
Run SUM (Software Update Manager) for automation.
Testing & Validation
Conduct integration and regression testing.
Validate business processes post-upgrade.
Go-Live & Monitoring
Execute a controlled go-live process.
Monitor system performance and resolve issues.
SAP BASIS Migration: Best Practices
Migrating an SAP BASIS system requires careful planning and execution to minimize downtime and ensure data integrity. Below are some best practices to follow for a smooth migration process:
1. Use DMO (Database Migration Option) for SAP HANA Migrations
Database Migration Option (DMO) is a feature of the Software Update Manager (SUM) that simplifies the migration process by combining the upgrade and database migration into a single step. This reduces overall downtime and eliminates the need for separate upgrade and migration activities.
Ensures a seamless transition from legacy databases to SAP HANA.
Reduces manual effort by automating several migration tasks.
Minimizes risks by performing pre-checks and validations before migration.
2. Optimize Downtime with Near-Zero Downtime Techniques
Minimizing system downtime is crucial for business continuity. Several techniques can be used to reduce downtime:
Parallel Processing: Splitting migration tasks into parallel streams to speed up execution.
Near-Zero Downtime Maintenance (NZDM): Enables business processes to continue running while critical database operations are performed in the background.
System Replication: Helps maintain a standby system that can take over in case of failure, reducing unplanned downtime.
3. Perform OS/DB Migration Checks Using SAP Tools
Before migration, thorough compatibility and performance checks should be conducted to prevent issues during the transition. SAP provides various tools to assist in this process:
SAP Readiness Check: Assesses system compatibility with the target environment.
SUM (Software Update Manager) with DMO: Automates the upgrade and migration process.
SAP Database Migration Factory: Provides a structured framework for large-scale database migrations.
Landscape Transformation (SLT) Replication: Ensures real-time data synchronization between systems.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can achieve a smooth SAP BASIS migration while maintaining system stability, security, and performance.
Certification: Why It Matters?

Earning an SAP BASIS Certification can significantly boost career prospects. With increasing demand for SAP professionals, expertise in system administration, performance tuning, and security management is highly valuable. This certification validates a professional's ability to manage SAP environments efficiently, making it a sought-after credential in the industry.
Top Benefits of Certification:
Industry-Recognized Expertise – Demonstrates proficiency in SAP system administration, upgrades, and security management.
Higher Salary Prospects – Certified professionals often command better salaries compared to non-certified peers.
Global Job Opportunities – SAP-certified professionals are in high demand across industries worldwide.
Enhanced Career Growth – Certification opens doors to senior roles such as SAP BASIS Administrator, Consultant, and Architect.
Certification Cost
The SAP BASIS Certification Cost varies depending on the level of expertise and training provider. Generally, the price range is as follows:
Associate Level – 30,000 - 50,000
Professional Level – 60,000 - 80,000
Expert Level – 1,00,000
Pursuing an SAP BASIS Certification ensures professionals stay ahead in the competitive IT landscape, equipping them with the necessary skills to manage SAP environments effectively.
Conclusion
Upgrading and migrating SAP BASIS systems require a strategic approach, encompassing thorough planning, precise execution, and continuous monitoring. Whether you are an experienced SAP administrator or an aspiring professional, expertise in SAP BASIS remains highly sought after in the global market. Mastery of performance tuning, security management, and cloud migrations enhances professional growth and opens new career opportunities.