Beyond Dawlish
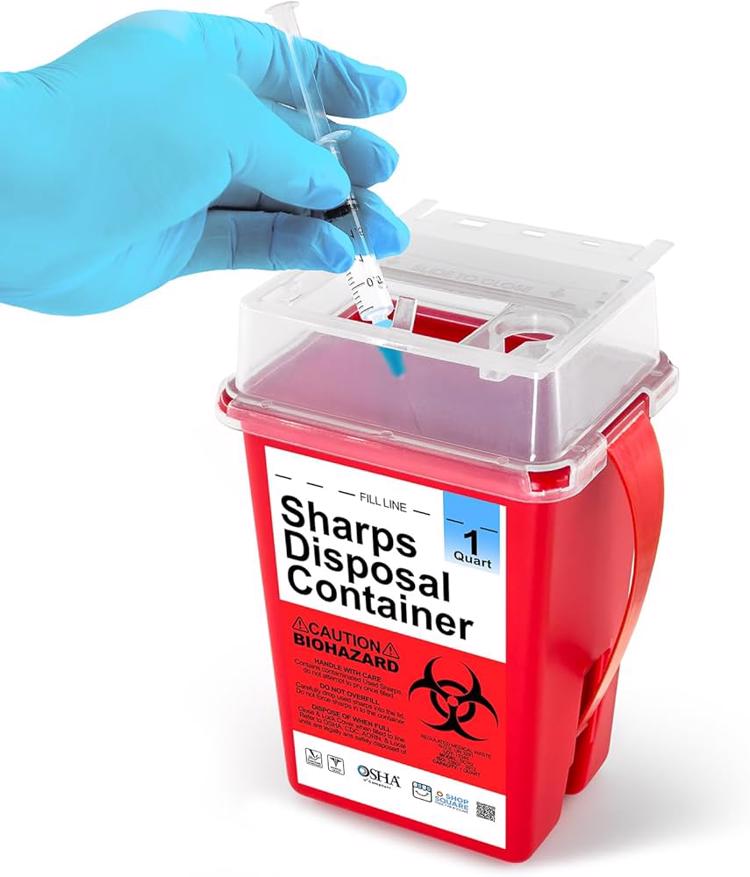
Needle waste disposal is a critical aspect of healthcare and public safety protocols, ensuring the proper management of medical sharps to prevent injuries and minimize environmental impact. This comprehensive guide explores the essential practices, regulations, and safety measures involved in needle waste disposal.
Understanding Needle Waste
Needle waste, also known as sharps waste, encompasses used needles, syringes, lancets, and other sharp medical instruments that have been in contact with bodily fluids or medications. Due to their potential to transmit infections and cause injuries, proper disposal is crucial.
Importance of Proper Disposal
Improperly disposed needles pose significant risks to healthcare workers, waste handlers, patients, and the community at large. Injuries from sharps can lead to infections such as hepatitis B and C, HIV, and other blood-borne diseases. Additionally, contaminated needles can pollute the environment if not disposed of correctly, posing risks to wildlife and public health.
Regulatory Framework
The disposal of needle waste is governed by strict regulations to ensure safety and compliance. These regulations are typically enforced at both federal and state levels and may include guidelines for packaging, labeling, transport, and treatment of sharps waste. Healthcare facilities, pharmacies, and other generators of medical waste must adhere to these regulations to mitigate risks effectively.
Best Practices for Needle Waste Disposal
Segregation: Separate sharps waste from other medical waste at the point of generation using designated containers that are puncture-resistant and leak-proof.
Containerization: Use FDA-approved sharps containers that are properly labeled with the biohazard symbol. Containers should be closable, sturdy, and resistant to puncture.
Fill Level Monitoring: Containers should not be overfilled. Once they are three-quarters full, they should be sealed, labeled, and removed from service for disposal.
Disposal Methods: Depending on local regulations and facilities' capabilities, needle waste may be treated through autoclaving, incineration, or other approved methods to render it safe for final disposal.
Transportation: Sharps containers must be handled with care during transport to prevent spillage or injury. Use certified medical waste transport services or follow applicable guidelines for safe transport.
Training and Education
Healthcare personnel and waste handlers should receive training on proper needle waste disposal practices, including handling, storage, and emergency response procedures. Regular training updates ensure compliance with current regulations and enhance safety awareness.
Environmental Impact
Proper disposal of needle waste reduces environmental contamination risks. Incineration and other treatment methods help destroy pathogens and minimize the release of pollutants into the air, water, and soil.
Effective needle waste disposal is essential for protecting healthcare workers, patients, and the environment from the risks associated with sharps injuries and contamination. By following regulatory requirements, implementing best practices, and providing ongoing training, healthcare facilities can ensure safe and compliant management of needle waste, contributing to overall public health and safety.
Adherence to regulatory guidelines and implementation of best practices are fundamental in the safe management of needle waste. By prioritizing safety, healthcare facilities can mitigate risks, protect personnel and the community, and contribute to environmental stewardship.




